Chapter 1 Daily Activities
Gambar
We do many kinds of activities everyday. In this chapter we will talk
about how to express our daily activities as part of our lives, such as
going to school., reading newspaper/books, playing some sports, hanging
out with friends or family ansd so forth. Activity that we do in our
daily life can be our hobby. We do this hobby in a happy way for sure as
it closely related to positive feeling. This chapter will also discuss
some common conversational English dealing with hobbies and interests.
Enjoy the lesson.
| Learning Purposes: |
Quote of the chapter |
After learning this chapter, you should be
able to:
- Understand daily activity conversations;
- Understand the pattern of “yes-no” questions in the context of
daily activities;
- Understand questions and answers about daily activities;
- Identify words and expressions used to talk about hobbies and
interest;
- Understand and practice expressions of handling guest;
|
“Invest in yourself. In your education.
There’s nothing better.”Syivia Porter. |
Word Pack: Hobbies
Classify these hobbies into the suitable column, which are mostly
pursued by men and which are mostly pursued by women.
modeling sewing
cooking creative writing
camping hiking car
designing horse riding
bird watching ice skating
paragliding cake decorating
Listening
[1]a. Listen to the dialogue read by your teacher. Then
complete the missing words.
Edi : Hello Irfan.
Irfan : Hi Edi.
Edi :
(1)______are you doing?
Irfan : I want to
(2) ____________with my father.
Edi :
(3) _____ you usually going fishing on holiday?
Irfan : Yes, my father
(4) ____ takes me with him. And I
(5)
_______to go fishing with him.
Edi :
(6) _____ your father also
(7) _____
palying tennis?
Irfan :
(8) ____, he
(9) _________ to play
tennis.
Edi : I like playing tennis
(10) ______.
Irfan : Oh, my father
(11) ________tennis every
(12) _________
and
(13) ____________.
Edi : So, he plays tennis
(14) ______a week.
(15) ______does
he usually play tennis?
Irfan : He usually plays in Manahan with his friends.
Edi : You don’t like playing tennis,
(16) _____ ?
Irfan : No, I
(17) _____ playing
(18) ___________
.
Edi : Well, that’s also a nice sport.
Irfan : Yes, I sometime play tennis with my brother.
Edi : I haveto go now.
Irfan :
(19) _______are
(20) ____________ ?
Edi : I
(21) _______________ go
(22) _____.
Goodbye.
Irfan : Okay, see you.
b. Answer these questions based on the dialogue.
- Where are irfan and his father going to go ?
- How many times does Irfan’s father play tennis ?
- Where does he usually play tennis ?
- Does Irfan also like to play tennis ?
- What kind of sport does Irfan like ?
- What kind of sport does Edi like ?
- Why does Edi leave Irfan ?
[2] Listen to the dialogue about heandling guest then
answer the following questions.
- How many people are talking in the dialogue ? Who are they ?
- From which company the guest is ?
- Is the manager available in the office ?
- When is the appointment should be ?
- In what way does the secretary handle the guest ?
Speaking
[3] Everybody has many different kinds of daily
activities to do everyday.
Now find somebody in your class who:
- sometimes get up late.
- always gets up before 5 o’clock every morning.
- goes to school bt motorcycle.
- goes to school by bus.
- never come to school late.
- always does the homework.
- usually watches television after school.
- always help the parents at home.
- always goes to sleep late at night.
Ask your classmate using “Do you…?” and make the list in the table
bellow.
| No. |
Question (Do You … ) |
Name |
a.b.c.
d.
e
f.
g.
h.
i. |
Do you sometimes get up late ? |
Adi, Asti, lusy, etc. |
[4] Study and practice these dialogue then answer the
questions that follow.
Dialogue 1
Joe : Where’s Sally in the afternoon ?
Alin : She’s at the university.
Joe : Is she afternoon ?
Alin : Yes, most of the afternoon.
Joe : Umm … do you know what is her hobby ?
Alin : She has many hobbies, such as reading novel and watching
Korea film. On Saturday she usually goes to bookstore to read or buy
some novels. Whilst on Sunday she sometimes helps her mother to cook.
Joe, I’m curious why you asked question ? Huh ?
Joe : Oh, nothing. I just want know more about her.
- What does Sally do?
- Where is Sally in most of the afternoon?
- What does Sally do you think?
- What are Sally’s hobbies?
- What do you think the reason behind Joe asked Alin about Sally’s
hobbies?
Dialogue 2
Linda : Hello, Mrs. Edward. How’s Evan?
Mrs. Edward : Oh, he’s fine.
Linda : What’s he doing these days?
Mrs. Edward : He’s working and going to school.
Linda : Where’s he working?
Mrs. Edward : At his uncle’s store. Why don’t’t you call him sometime?
Linda : Is he there all days?
Mrs. Edward : No, only part of the day. He’s there two hours in the
morning and two hours in the afternoon.
Linda : What’s the number at the store?
Mrs. Edward : Let me check first. Hmm … It’s 794 8163
- What is the relationship between Evan and Mrs. Edward you think?
- What does Evan do besides working?
- Where does Evan go to work?
- What about Evan’s work hour?
- Do you think linda will call Evan through the store’s line?
[5] Make a group pf two then make a dialogue about
yourdaily activities.
Ask your friend about what he/she does everyday by using this
model:
A : What do you usually do in ……… ?
B : I usually ……..
(You are asked to be creative to make your own model of dialogue)
[6] Role playing th dialogue in front of the class.
Situasion: Mr. Roger comes to front desk for setting his
account. He will check out now so he pays his bill. Front desk agent
finishes checking out procedure.
Front Officer : Good morning, Sir, Can I help you?
Mr. Roger : Yes please. I would like to check out today.
Front Officer : OK Sir. Hmm … May I ask your name and room number,
Sir?
Mr. Roger : I am Roger Wolfgang and I am from room no. 803.
Front Officer : Wait a minutes Sir. Yes, Mr. Robert. You are from room
no. 803 and you would like to check out todsy, right?
Mr. Rogeres : Yes.
Front Officer : Sir, have you used any of our service today?
Mr. Regar : No, Not all.
Front Officer : Hmm … OK Sir. Here is your bill now. For 4 night you
have been charged for$400. $100 for each night and other cost is for
laundry and room service you made during this time. In total your bill
is $512.
Mr. Regar : Let me check my bill, please.
Front Officer : Sure Sir. No problem. Take your time.
Mr. Regar : OK. I gues everything is OK. Now, I like to pay by
credit card. Any problem ?
Front Officer : No at all. May I have your card, please?
Mr. Regar : Here it is.
Front Officer : Please sign your name here, Sir.
Mr. Regar : OK. One more thing. I will leave the room now, but
one my friend will come at 2 p.m. Can I wait him in your lobby?
Front Officer : No problem at all Sir.
Mr. Regar : Your welcome Sir. Have a nice day.
Functional Skill
- Some common conversational English dealing with dally activities.
| Asking daily activities |
Responding |
- What time do you get up?
- What time is breakfast at your house?
- What do you usually do in the afternoon?
- What do you generally do over the weekend?
- Do you ever go to museum?
- What kinds of things do you like to see?
- Do you ever listen to the radio?
- Do you watch television very often?
- I get up about seven fifteen.
- Breakfast is always at a quartener to eight.
- I usually study or read.
- We generally enjoy sports and visits friends.
- I go every seeing statues and old paintings.
- Well, I sometimes watch TV in the evening.
- Certainly. In fact, I listen practically every night
- I like the Eleven O’clockt theater best of all.
|
|
Note : We use simple present tense to express something that
happens repeatedly. We also use simple present to talk about our daily
activities.
- Some common conversational English dealing with hobbies and
interests.
- Some common conversational English in handling guest, mainly in
front desk or lobby area.
- Good morning/afternoon/evening. Receptionist/Information speaking.
May I help you?
- Good morning/afternoon/evening, Sir/Madam. Welcome to our hotel?
- How may I help you ?
- May I have your name please? How do you spell that?
- Would you please fill in the registration form?
- Here is the pen Mr. Andy.
- Could you wait a few minutes?
- Would you mind going/stepping over to the-desk at the end of the
counter?
- We are looking forward to seeing you again soon.
- Certainly, you may leave a message.
To response, we may use these following expressions:
- Good morning/afternoon/evening.
- Yes of course.
- Thank you in advane
- No, thanks.
- Yes, I have an appointment withMr. Lee.
- A cup of coffee, please.
- I would like to see your manager.
|
|
Reading
[7] a. Read the text carefully.
Schooling Time
I live near from the school. I go to school by car at 06.00 am. Every
Monday, we start the school with an assembly. The teacher announces or
gives us some information about the school’s event.
The lesson begins at 07.00 am. I have 6 subjects. We all study the
same subjects, except for English class. I have to learn English every
day. The lessons end at 03.00 pm, but we go home early on Friday.
We have 15 minutes for break in the morning and in the afternoon. The
first break is at 10.00 am and the next break is at 01.15 p.m. We also
have break at lunch time. Some students bring their own meal. I just eat
my snack.
At the end of the school, I go home and take a nap at home ar watch
television. Most of the time, I do my homework. I have lots of homework.
Sometimes, I forger to do my homework or I am lazy to do it.
b. Answer these questions based on the text you have just read.
- Where does the writer live?
- What time does she go to school every day?
- How does she go to school?
- What does her school start?
- How many times does she get break time?
- What do the students do when the lunch break?
- How about the writer?
- What does the writer do after getting home?
- What does the writer some times forget to do her homework?
- What kind of student do you think is she?
c. Find the opposite meaning of these words in the text.
|
|
|
far > <
___________________________________________________________
take > <
___________________________________________________________
end > <
___________________________________________________________
different > <
___________________________________________________________
late > <
___________________________________________________________
less > <
___________________________________________________________
remember > <
___________________________________________________________
|
|
[8] a. Read the text to answer the questions.
|
|
|
Hobbies
Hobbies are spare-time pursuits. A hobby can be very satisfying an
fulfilling – a stress busfer that can relieve you of all the trials and
tribulations of modern day life. In fact, engaging in a hobby can also
lead to enhance skills, knowledge and experience. But the sheer pleasure
that the hobbyist deriver out of it is the driving force. Pursuing a
hobby can be calming and therapeutic. Cooking, gardening, collecting,
astronomy, painting, writing – the list is andless. Hobby photographere
and astronomers may even go on to make a profession out of it. Hobby
photographere can be amateur shutterbugs clicking for family albums or
those wanting to capture the beauty of nature through the lens eyes.
|
|
b. Answer these questions based on the text.
- How many kinds of hobbies mentioned in the text? What are they?
- From those hobbies, is therea hobby that you have too?
- What can you get from doing your hobby?
- In what way can make our money from our hobbies? Give an axample!
Gerund
A gerund is a verb. Due to a certain case, added by the suffix –
ing
(Verb –ing). A gerund is also known as a verb that funxtions like a
noun.
The use af Gerund :
Gerund as a Subject
Examples :
- Swimming is good sport.
- Cooking is not difficult.
- Smoking is not good for your health
Gerund as a Object
Examples :
- My hobby is playing badminton.
- Mary is interested in reading novel.
- John loves traveling.
Gerund used after preposition (in, on, at, of, before, without,
by, etc)
Examples:
- Before going bed we must pray to God.
- In studying foreign language we must have a dictionary.
- After having dinner last night we went to the movie.
Gerund always appears aftercertain verbs:
Examples:
- Why do you always avoid meeting her?
- We consider going to attend the party next week.
- I enjoy studying English with Mr. Yusuf.
- John and Marry stopped talking to each other since yesterday.
- He admits to going with me to the party.
Gerund used after certain expression:
Examples:
- It is no use regretting something that has happened.
- Let’s go shopping.
- She can’t help crying when she heard the bad news.
-
- Gerund after possessive
pronoun
Examples:
- Your coming to your house made her happy.
- His leaving made her sad.
- The teacher doesn’t like our coming late.
[9] Put the vaerb in the bracket in the right form.
- I enjoy (dance) because it’s my hobby.
- I am keen on (work) in the computer industry.
- Do you mind (help) me wash the dishes?
- I learnt (swim) when I was five years old.
- Have you finished (clean) the kitchen?
- John apologized for (interrupt) me.
- I’m interested in (study) other countries and their culture.
- Are you interested in (live) in Africa?
- Students practise written English by (write) compositions.
- Daniel improves his English by (watch) a lot of English TV programs.
- 2. Interrogative Sentence (Questions)
There are three types of questions in English:
- a. Verbal Questions (Yes/No Question)
Verbal Questions or
Yes/No Question is a question that
requires only “Yes” or “No” for the answer. This question is started by
to be, auxiliary verb or to do.
Examples:
(+) They are Canadian.
(?) Are they Canadian?
Answer:
Yes they are or No they aren’t.
1) If the main verb of the sentence is “to be”, simply invert
the subject and the verb “to be” :
Examples:
- They are Canadian. —
Are they Canadian?
- They are friendly. –
Are they friendly?
2) If the sentence includes a main verb and another or other
helping (auxiliary) verb(s), invert the subject and the (first) helping
(auxiliary) verb.
Examples:
- They are visitng
Perth. – Are they visiting
Perth?
- She has done the
homework. – Has she done
the homework?
- Freddy has been
sleeping all day long. – Has
Freddy been slepping all day long?
- She will be
reading magazine. – Will
she be reading the magazine?
3) If the sentence includes a verb which is not the verb “to be”
and doesn’t include a helping (auxiliary) verb, the transformation is
more complex.
a) If the verb is in the present tense, add either
do or
does
and put the main verb in its base form:
- do if the subjecs is the first person singular, second person
singular, first person plural, second person plural and third person
plural (I, you, we. They)
Examples:
- I like durians. – Do you like durians?
- They go to school by train. – Do they go to
school by train?
- does if the subject is the third person singular (he, she,
it).
Examples:
- Noni eats a lot. – Does Noni eat a lot?
- She dislikes volleyball. – Does she dislike volleyball?
b) If the verb is in the past tense, add
did and put the
main verb in its base form:
Examples:
- She uncovered the secret. – Did she uncover the
secret?
- She wrote a nice report. – Did she write a nice
report?
- They did the homework. – Did they do the
homework?
- b. Pronominal question (Wh. Question)
Pronominal Question or Wh. Question is a question that
requires an answer in the form af statement. This kind of question is
started by question is started by question word such as
who, what,
where, when, why, which, and
how.
| Wh. Questions |
Asking about |
Examples |
| Who |
person |
Who’s that? That’s Emil. |
| Where |
place |
Where do you come from? I am from Toronto. |
| Why |
reason |
When do you like reading? Because
it broadensmy insight. |
| When |
time |
When do you get up in the morning?
At 05.00. |
| How |
manner |
How do you go to Surabaya? By
plane. |
| What |
object, idea, or action |
What do you do? I’m an architect. |
| Which |
choice |
Which one do you want to buy? The blue
one. |
| Whose |
possession |
Whose is this car? It’s Tom’s. |
| Whom |
object of the verb |
Whom did you meet? I meet the supervisor. |
| What kind |
description |
What kind of film do you like? I
like comedy. |
| What time |
time |
What time do you come home? At 6
pm. |
| How many |
quantity (countable) |
How many staffs in HRD? There are twelve. |
| How much |
amount, rice (uncountable) |
How much time have we got? An
hour. |
| How Long |
Duration, length |
How long did you live in Macau? For one
week. |
| How often |
Frequency |
How often do you go swimming? Once
a week. |
| How far |
Distance |
How far is your office? It’s two
miles far. |
| How old |
Age |
How old your brother? He’s 10. |
| How come |
Reason |
How come I didn’t see at the
concert? |
[12] a. Make the correct question words.
- ______ do he live? – He live in London.
- ______’s that boy? – He’s my brother.
- ______ do you go to school? – By bus.
- ______ does the post office open? – At eight O’clock.
- ______ are you wearing that coat? – Because it’s hot!
b . Question Tag Question
Question Tag is used to ask for an agreement or certainly of
what someone said. In the Question Tag, if the Statement is Positive the
Tag must be in Negative form. If the statement Negative, the Tag must
be in Positive form.
1) Statement
Example:
- Ron peels an apple everyday, doesn’t he?
- Etik will wash the clothes, won’t she?
- Sinta was absent yesterday, wasn’t she?
- They did not sleep here last night, did they?
Note:
a) In Question Tag, the Tag always in the Contracted Form.
Examples:
- Are not = aren’t
- Can not = can’t
b) Subject in the tag is always in the form of Pronoun.
Example:
- Yuli joins the game, doesn’t she ?
c) These words have negative meaning in a sentence:
No one, no body, nothing, never, hardly, seldom, rarely. None.
Neither
Example:
- Hadi never comes late, does he?
- No one is in the class room, are they?
d) For positive sentence that use verb “am” the Tag use “aren’t”.
Example:
Compare these two sentences:
- I am not your teacher, am I ?
- I am your teacher, aren’t I ?
2) Imperative
In imperative sentence, we use “Will you” or “Shallwe” as the TAG.
Examples:
- Open the window, will you ?
- Don’t open the door, will you ?
- Let’s finish the work together, shall we ?
3) Too – Enough
- a. Too
It show something that has negative meaning.
Too is placed
before an Adjective.
Examples:
- I am very tired. I can’t study.
=
I am too tired to study.
- The box is heavy. He can’t lift it.
=
The box is too heavy for him to lift.
- b. Enough
Is the opposite of
Too. It has positive meaning.
Enough is
placed after an adjective.
Examples:
- Merry is well now. She can come to school.
=
Merry is well enoughto to go to school.
- The lake is deep. We can swim in it.
=
The lake is deep enough to swim in it.
[13] Complete the following Question Tag Question.
- Stefan was ill last week, _____ ?
- I am the winner, _____ ?
- You are no happy _____ ?
- Linda paid three dollars for your hat, ______ ?
- Tuti will clean the floor, _____ ?
- They have eaten up all rice, ______ ?
- Don’t leave the bag there, ______ ?
- Clean your shoes, _______ ?
- Be a good student, ______ ?
- Ani borrow Rita’s car, ______ ?
|
|
[14] Combine the sentence using Too or Enough.
- Merry is very sick. She can’t go to school.
- The moon is very bright. We can read a book by it.
- John is tall. He can reach the ceiling.
- The exercise is very easy. We can do it.
- The leason is very difficult. I can’t understand it.
- Astrid is very beautiful. She can be a supermodel.
- The problem is very complicated. We can’t solve it.
- The rain is very hard. We can’t go home.
- It is a nice song. I can listen to this song everyday.
- The car is very expensive. I won’t be able to buy it.
Writing
[15] Translate these sentence into English.
- Apakah kereta api itu akan segera berangkat ?
- Apakah Tessa dapat memimpin organisasi ini?
- Apakah hujan turun tadi malam?
- Kapan Arif akan menggoreng ikan itu?
- Berapa lama kamu mengerjakan PR tadi pagi?
- Berapa banyak buku yang kamu jual hari ini?
- Apakah saya dapat menunggu kamu sebentar?
- Mengapa kamu tidak jujur?
- Dimanakah rumahmu?
- Apakah rumah yang besar itu mahal harganya?
[16] Write your friend’s schedule in this table. Don’t
forget to ask your friend by using
Interrogative sentences.
Name: ______________
| Time |
Sunday |
Monday |
Tuesday |
Wednesday |
Thursday |
Friday |
Saturday |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[17] Write a paragraph about your own daily activities with
your own words in your workbook. You can add information on things that
you usually, always, sometimes, or never do in your spare ime or in
your holiday.
Summary
- 1. Some common conversational English dealing with
daily activities.
| Asking daily activities |
Responding |
· What time do you get
up ?· What time is breakfast at your house ?· What do
oyu usually do im the afternoon ?· What do you generally do
over the weekend?· Do you ever go to museum?
· What kinds of things do you like to see?
· Do you ever listen to the radio?
· Do you watch television very often? |
· I get up about seven
fifteen.· Breakfast is always at a quarter to eight.· I
usually study or read.· We generally enjoy sports and visits
friends.· I go every now and then.
· I enjoy seeing statues and old paintings.
· Well, I sometimes watch TV in the evening.
· Certainly. In fact, I listen practically every night.
· I like the ElevenO’clock theater best of all. |
- 2. Some common conversational English dealing with
hobbies and interests.
Asking hobbies and interests:
· What is your hobby?
· Do you like playing chess?
· What is your favorite book to read?
· Do you delight in hiking?
Hobbies are closely related to positive feelings and are expressed
through verbs and phrases like:
· I enjoy.
· I love gardening.
· I am thrilled about collecting sweet wrappers.
· I relax with a book whenever I find time.
- 3. Some common conversational English in handling
guest, mainly in front desk or lobby area.
· Good morning/afternoon/evening, Sir/madam. Welcome to our
hotel.
· How may I help you?
· May I have your name please? How do you spell that?
To response, we may use these following expressions:
· Good morning/afternoon/evening.
· Yes of course.
· Thank you in adveance.
· No, thanks.
- 4. Gerund
a gerund is a verb, due to a certain case, added by the suffix –
ing
(Verb –
ing). A gerund is also known as verb that functions
like a noun.
Examples:
·
Swimming is a good sport.
·
My hobby is playing badminton.
·
Why do you always avoid meeting her?
- 5. Interrogative sentence (Question)
There are types of questions in English:
- a. Verbal Question (Yes/No Question)
Verbal Question or
Yes/No Question is a question that
requires only”Yes”or “No” for the answer.
Examples:
· Affirmative: They are Canadian
· Interrogative (Yes/No question): Are they Canadian?
· Answer: Yes, they are No, they aren’t.
- b. Pronominal question (Wh. Question)
Pronominal Question or Wh. Question (Who, Where, Why, When,
How, What, Which, Whose, Whom) is a question that requires an answer in
the form of statement. Asking about: person, place, reason, time,
manner, object, idea, or action, choice, possession, object of the verb.
Examples:
- Who’s that? That’s Emil.
- Where do you come from? I am from Toronto.
- What do you do? I’m an architect.
- c. Question Tag Question
Question Tag is used to ask for an agreement or certainly of
what someone said. In the question tag, if the Statement is positive the
Tag must be in Negative form. If the statement Negative the Tag must be
in Possitive form.
Example:
- Etik will wash the clothes, won’t she ?
- Yuli join the game, doesn’t she?
- Too – English
- a. Too
It show something that has negative meaning.
Too is placed
before an Adjective.
Example: It is too difficult to do for a little child.
- b. Enough
Is the opposite of
Too, it has positive meaning. Enough is
placed after an Adjective.
Example: I still have
enough time to prepare dinner.

 UNAS 2011;
UNAS 2011;
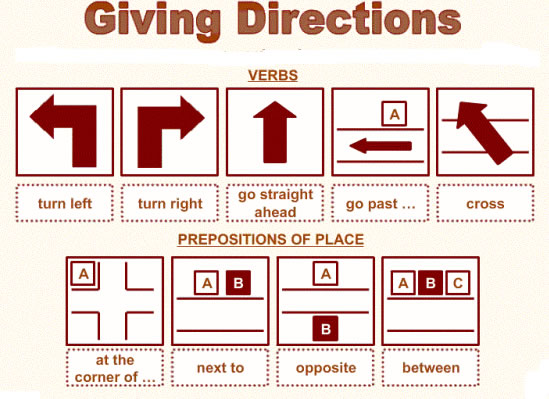
 Go straight on till you see the
hospital then turn left.
Go straight on till you see the
hospital then turn left.